- Home
- News
- What Are The Five Main Components Of A Machine Vision System? Which Kind Of Lens Is Used In Machine Vision Systems? How To Choose A Lens For Machine Vision Camera?
What Are The Five Main Components Of A Machine Vision System? Which Kind Of Lens Is Used In Machine Vision Systems? How To Choose A Lens For Machine Vision Camera?
1、What is the machine vision system?
A machine vision system is a type of technology that uses computer algorithms and imaging equipment to enable machines to perceive and interpret visual information in the same way that humans do.
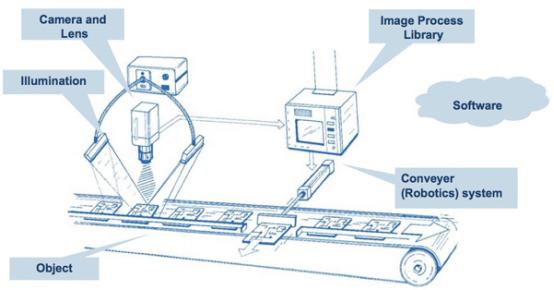
The system consists of several components such as cameras, image sensors, lenses, lighting, processors, and software. These components work together to capture and analyze visual data, enabling the machine to make decisions or take actions based on the analyzed information.
A machine vision system
Machine vision systems are used in a variety of applications such as manufacturing, robotics, quality control, surveillance, and medical imaging. They can perform tasks such as object recognition, defect detection, measurement, and identification, which are difficult or impossible for humans to perform with the same accuracy and consistency.
2、The five main components of a machine vision system are:
- Imaging hardware: This includes cameras, lenses, filters, and lighting systems, which capture visual data from the object or scene being inspected.
- Image processing software: This software processes the visual data captured by the imaging hardware and extracts meaningful information from it. The software uses algorithms such as edge detection, segmentation, and pattern recognition to analyze the data.
- Image analysis and interpretation: Once the image processing software has extracted the relevant information, the machine vision system uses this data to make decisions or take actions based on the specific application. This includes tasks such as identifying defects in a product, counting objects, or reading text.
- Communication interfaces: Machine vision systems often need to communicate with other machines or systems to complete a task. Communication interfaces such as Ethernet, USB, and RS232 enable the system to transfer data to other devices or receive commands.
- Integration with other systems: Machine vision systems may be integrated with other systems such as robots, conveyors, or databases to form a complete automated solution. This integration can be achieved through software interfaces or programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
3、Which kind of lens is used in machine vision systems?
Machine vision systems typically use lenses specifically designed for industrial or scientific applications. These lenses are optimized for image quality, sharpness, and contrast, and are built to withstand harsh environments and frequent use.
There are several types of lenses used in machine vision systems, including:
- Fixed focal length lenses: These lenses have a fixed focal length and cannot be adjusted. They are typically used in applications where the object distance and size are constant.
- Zoom lenses: These lenses can adjust the focal length, allowing the user to change the magnification of the image. They are used in applications where the object size and distance vary.
- Telecentric lenses: These lenses maintain a constant magnification regardless of the object distance, making them ideal for measuring or inspecting objects with high accuracy.
- Wide-angle lenses: These lenses have a larger field of view than standard lenses, making them ideal for applications where a larger area needs to be captured.
- Macro lenses: These lenses are used for close-up imaging of small objects or details.
The choice of lens depends on the specific application and the desired image quality, resolution, and magnification.
4、How to choose a lens for machine vision camera?
Choosing the right lens for a machine vision camera is crucial to ensure the best possible image quality and accuracy for your application. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a lens:
- Image sensor size: The lens you choose must be compatible with the size of the image sensor in your camera. Using a lens that is not optimized for the image sensor size can result in distorted or blurred images.
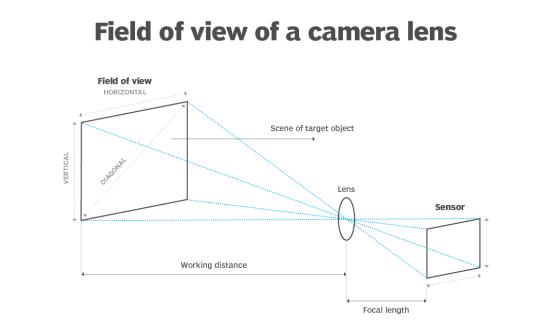
- Field of view: The lens should provide the desired field of view for your application. If you need a larger area to be captured, a wider angle lens may be necessary.
Field of view of a camera lens
- Working distance: The distance between the lens and the object being imaged is called the working distance. Depending on the application, a lens with a shorter or longer working distance may be required.
The working distance
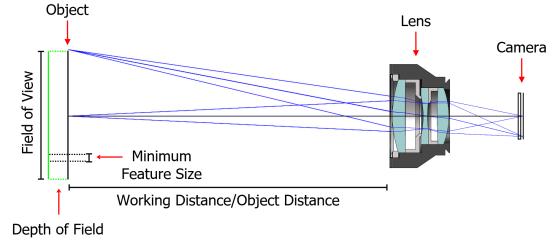
- Magnification: The lens magnification determines how large the object appears in the image. The required magnification will depend on the size and detail of the object being imaged.
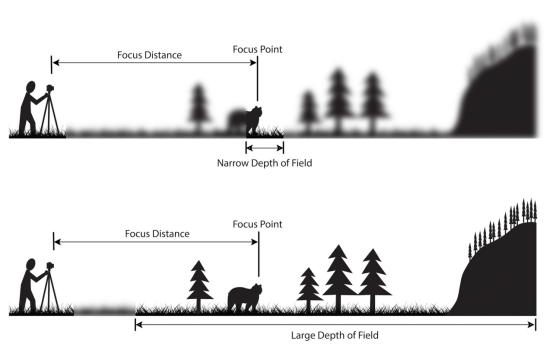
- Depth of field: The depth of field is the range of distances that are in focus in the image. Depending on the application, a larger or smaller depth of field may be necessary.
The depth of field
- Lighting conditions: The lens should be optimized for the lighting conditions in your application. For example, if you are working in low light conditions, a lens with a larger aperture may be necessary.
- Environmental factors: The lens should be able to withstand the environmental factors in your application, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration.
Considering these factors can help you choose the right lens for your machine vision camera and ensure the best possible image quality and accuracy for your application.